Ketamine Products for Sale on the Dark web
What is Ketamine?
Ketamine is a dissociative anesthetic that has both medical and recreational uses. It was first synthesized in the 1960s and has since found applications in anesthesia, pain management, and, more recently, as a treatment for certain mental health conditions. In recreational settings, ketamine is sometimes used for its hallucinogenic effects. Here are key aspects of ketamine:
Medical Use: Ketamine is used as an anesthetic in medical and veterinary settings. It induces a trance-like state while providing pain relief and memory loss. Additionally, ketamine is employed in emergency medicine for its rapid onset and short duration of action.
Dissociative Anesthetic: Ketamine is classified as a dissociative anesthetic because it can cause a sense of detachment from reality, leading to a feeling of dissociation from one’s body or surroundings. It operates by blocking the NMDA receptor, which is involved in the perception of pain and sensory experiences.
Recreational Use: In recreational contexts, ketamine is sometimes used for its hallucinogenic and dissociative effects. It can produce altered perceptions of sight and sound, a sense of floating or detachment, and vivid dream-like experiences. The use of ketamine for non-medical purposes is associated with risks, including adverse reactions and potential harm.
Therapeutic Use: Ketamine has gained attention for its potential therapeutic effects, particularly in the treatment of certain mental health conditions. It is being explored as a treatment for depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Some clinics offer ketamine infusion therapy for these purposes.
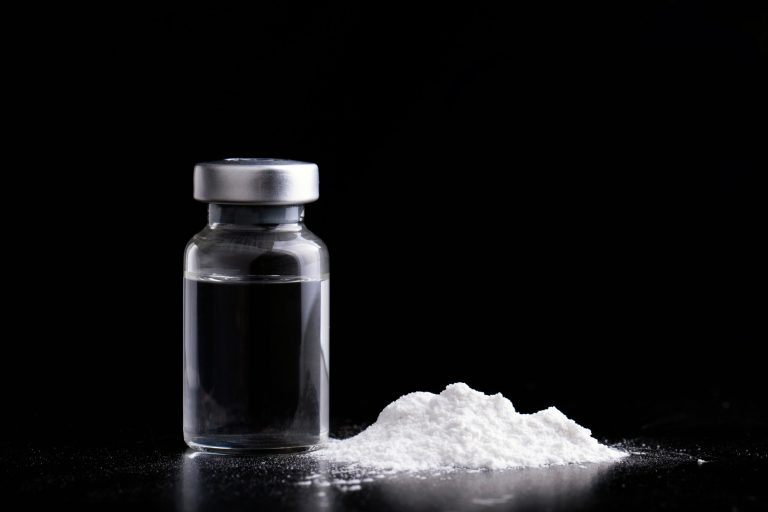
Dosage Forms: Ketamine is available in various forms, including a liquid for intravenous (IV) administration in medical settings, as well as a powder or crystalline substance for recreational use. In recreational settings, ketamine is often snorted or taken orally.
Side Effects: The use of ketamine can lead to various side effects, including confusion, hallucinations, nausea, and changes in perception. Higher doses or misuse can lead to more severe reactions, including respiratory distress, delirium, and in extreme cases, a state referred to as the “K-hole,” characterized by profound dissociation.
Dependence and Addiction: Ketamine has the potential for psychological dependence and addiction, particularly with frequent and high-dose use. Individuals who misuse ketamine may experience cravings and a loss of control over their use.
Legal Status: The legal status of ketamine varies by country. In many places, it is a controlled substance, and its possession, distribution, and use for non-medical purposes can lead to legal consequences.
It’s important to note that the use of ketamine outside of medical supervision can be risky and may have adverse health effects. Any use of ketamine should be approached with caution, and individuals considering its use for therapeutic purposes should do so under the guidance of qualified healthcare professionals.
Psychedelic Mushrooms for Sale
-
Rated 4.20 out of 5 based on 5 customer ratings$365.00
-
Rated 4.80 out of 5 based on 5 customer ratings$190.00
-
Rated 5.00 out of 5 based on 2 customer ratings$90.00
-
Rated 5.00 out of 5 based on 4 customer ratings$700.00
-
Rated 4.60 out of 5 based on 5 customer ratings$95.00
-
Rated 4.60 out of 5 based on 5 customer ratings$230.00
-
Rated 4.20 out of 5 based on 5 customer ratings$350.00
-
Rated 4.60 out of 5 based on 5 customer ratings$250.00
History of Ketamine
The history of ketamine dates back to its discovery and development as an anesthetic in the mid-20th century. Here is an overview of the key milestones in the history of ketamine:
Synthesis and Discovery (1962): Ketamine was first synthesized in 1962 by American chemist Calvin Stevens at Parke-Davis Laboratories, a pharmaceutical company. The initial intent was to create a safer alternative to phencyclidine (PCP), a dissociative anesthetic.
FDA Approval and Medical Use (1970s): Ketamine was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1970 for medical use as an anesthetic. Due to its unique properties, such as rapid onset and relatively short duration, ketamine found applications in both human and veterinary medicine.
Emergence of Recreational Use (1970s-1980s): In the 1970s and 1980s, ketamine started to gain popularity as a recreational drug due to its dissociative and hallucinogenic effects. It became known by various street names, including “Special K.”
Therapeutic Potential for Mental Health (21st Century): In the 21st century, there has been a growing interest in the potential therapeutic applications of ketamine for mental health conditions. Research studies and clinical trials have explored its effectiveness in treating depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and other mood disorders. Ketamine infusion therapy has been offered in some clinics for these purposes.
Ketamine and Treatment-Resistant Depression (2010s): Ketamine gained attention for its rapid antidepressant effects in individuals with treatment-resistant depression. Some clinicians began administering ketamine off-label to patients who did not respond well to traditional antidepressants.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations: The recreational use of ketamine raised concerns about its potential for abuse and led to legal and regulatory actions in various countries. In many places, ketamine is a controlled substance, and its non-medical use is subject to legal consequences.
Research on Mechanism of Action (ongoing): Ongoing research continues to investigate the exact mechanisms of action by which ketamine produces its therapeutic effects. It is known to interact with the glutamate system in the brain, influencing neural plasticity and connectivity.
Concerns and Risks: The misuse of ketamine, especially in higher doses or without medical supervision, is associated with various risks, including hallucinations, disorientation, and physical harm. Long-term or frequent use can lead to psychological dependence and addiction.
Ketamine in Emergency Medicine: Ketamine remains an essential tool in emergency medicine due to its analgesic and dissociative properties. It is used for procedures requiring sedation, especially in cases where rapid onset and short duration of action are advantageous.
The history of ketamine reflects its evolution from a synthesized anesthetic to a substance with a complex profile of medical, recreational, and therapeutic applications. Ongoing research continues to explore the full range of its effects and potential benefits in various clinical contexts.
How to identify Ketamine Products
Identifying ketamine products, especially in non-medical or recreational settings, can be challenging as the substance may take various forms and is often encountered on the illicit market. Ketamine is typically found as a white crystalline powder, but it can also be liquid or in other formulations. Here are some considerations on how to identify ketamine products:
Physical Appearance:
- Powder Form: Ketamine is commonly encountered as a white or off-white crystalline powder. The powder may be clumpy or fine, depending on how it has been processed.
- Liquid Form: In medical settings, ketamine is often found in liquid form. On the illicit market, it may be dissolved in a liquid for easier transportation or administration.
Packaging and Containers:
- Vials: In medical settings, ketamine is often packaged in vials for injection. Illicit use might involve the repackaging of ketamine into smaller vials or containers.
- Bags or Wraps: On the street, ketamine might be sold in small plastic bags, wraps, or capsules. The packaging can vary widely.
Dosage Forms:
- Tablets or Capsules: In some cases, ketamine may be pressed into tablets or filled into capsules. However, it is less common compared to its powdered form.
- Blotter Paper: While more commonly associated with substances like LSD, ketamine has been reported to be impregnated onto blotter paper in some instances.
Color and Odor:
- Color: Pure ketamine is typically a white or colorless substance. Be cautious of any discoloration or impurities.
- Odor: Ketamine is known for having a distinctive odor, often described as a “medicinal” or “chemical” smell. However, the odor might be masked or altered if the substance is mixed with other compounds.
Testing Kits:
- Reagent Testing: Drug testing kits, such as reagent test kits, can help identify the presence of ketamine. These kits involve adding a small sample of the substance to a testing solution and observing a color change. Reagent tests are not foolproof but can provide some indication of the presence of specific substances.
Source and Reliability:
- Trustworthy Sources: If ketamine is obtained for medical or therapeutic purposes, it should come from a legitimate and reliable source, such as a licensed medical professional or pharmacy. Illicit sources can pose significant risks, including the potential for adulteration.
Legal Considerations:
- Legal Status: Ketamine is a controlled substance in many countries, and its possession, distribution, and use for non-medical purposes can lead to legal consequences. Understanding and adhering to local drug laws is crucial.
It’s important to note that identifying substances solely based on appearance can be unreliable, as illicit drugs are often adulterated or misrepresented. If someone suspects they have encountered ketamine or any other substance, using testing kits from reputable sources and seeking professional assistance are advisable for accurate identification and harm reduction. Additionally, engaging in open and honest communication with healthcare professionals is crucial if there are concerns about substance use.
Effects of Psychedelic Mushrooms
The effects of consuming ketamine can vary based on factors such as the dosage, individual tolerance, and the setting in which it is used. Ketamine is known for its dissociative and hallucinogenic properties, and its effects can be complex. Here are some of the common effects associated with ketamine use:
Dissociation: Ketamine is classified as a dissociative anesthetic, and one of its primary effects is inducing a sense of detachment or dissociation from one’s body and surroundings. Users may feel a sense of “floating” or being disconnected from reality.
- Hallucinations: Ketamine can cause hallucinations, leading to altered perceptions of sight and sound. Users may experience vivid and dream-like imagery.
Euphoria: Some individuals report feelings of euphoria and a sense of calm or relaxation during the early stages of ketamine use.
Analgesia (Pain Relief): Ketamine is an anesthetic, and as such, it can provide pain relief. In medical settings, it is used for its analgesic properties.
Distorted Perception of Time: Ketamine can alter the perception of time, making it feel either elongated or compressed.
Impaired Motor Function: Ketamine use can lead to impaired coordination and motor function. Users may experience difficulty moving or walking, commonly referred to as the “K-walk.”
Nausea and Vomiting: Some individuals may experience nausea and vomiting, particularly during the onset of the ketamine experience.
Increased Heart Rate and Blood Pressure: Ketamine use can lead to physiological changes, including an increase in heart rate and blood pressure.
Memory Impairment: Ketamine is associated with temporary memory impairment, and users may have difficulty recalling events that occurred during the intoxication period.
Cognitive Effects: Users may experience alterations in thought processes, including difficulty concentrating and maintaining a linear stream of thought.
K-Hole: In higher doses, users may enter a state known as the “K-hole,” characterized by a profound and more intense dissociative experience. In this state, individuals may have limited awareness of their surroundings and experience intense hallucinations.
It’s important to note that ketamine use is not without risks, and the effects can be unpredictable. Misuse or abuse of ketamine can lead to adverse reactions, including anxiety, paranoia, delirium, and in extreme cases, respiratory distress. Long-term or frequent use may result in psychological dependence and addiction.
Additionally, the context in which ketamine is used plays a significant role in shaping the overall experience. While some individuals may use ketamine recreationally for its dissociative effects, it’s important to be aware of the potential risks and to prioritize safety. Seeking professional guidance and using substances responsibly are crucial aspects of harm reduction.
Legal Status of Psychedelic Mushrooms
The legal status of psychedelic mushrooms varies widely around the world. In some countries and regions, the possession, sale, or use of psychedelic mushrooms is illegal and can result in serious legal consequences, including fines, imprisonment, and other penalties. In other places, there may be varying degrees of legality, such as decriminalization or specific regulations regarding their use.
It’s important to note that laws and regulations can change, and it’s crucial to be aware of the legal status in your specific location.
Illegal in Many Countries: Psychedelic mushrooms, specifically those containing psilocybin and psilocin, are illegal in numerous countries, including the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, and many others.
Decriminalization: In some places, there is a trend toward decriminalization, where the possession of small amounts of psychedelic mushrooms may be treated as a civil or minor offense rather than a criminal one. Decriminalization does not mean that the substance is legal, but it reduces the legal consequences for personal use.
Medical Use: Some jurisdictions are exploring or have already implemented laws allowing the medical use of psilocybin or psychedelic mushrooms under certain circumstances. This typically involves strict regulations and oversight by healthcare professionals.
Research Exceptions: In some cases, there may be allowances for the use of psychedelic mushrooms for scientific or research purposes under controlled conditions.
Always be aware of and comply with the laws in your specific location. Legal consequences can range from warnings and fines to more severe penalties such as imprisonment. It’s essential to prioritize safety, be informed, and make responsible decisions regarding the use of any substance, considering both legal and health implications.
Where to Ketamine Online
There are so many websites online that promise to sell Psychedelic Products online. Some of these websites deliver what they promise, others do not. If you are looking to buy psychedelic mushrooms online then look no further than dark web psychedelics website. In our shop, you will find a wide variety of psychedelic products, ranging from Mushrooms, LSD, MDMA and Ketamine We offer high quality psychedelic mushrooms carefully sourced from the best producers in the business of shrooms.
Contact us for more information on purchases. Our delivery system is discreet and 100% safe. Our clients safety and anonymity is our greatest priority.
Why buy Ketamine from Us
We offer a wide variety of Psychedelic Ketamine and other psychedelic products. Our products are high quality and of very high purity. We offer free delivery for bulk orders and we take our clients security and anonymity seriously. Shipments are handled discreetly with our clients addresses well protected.